Connected BIM
Connect BIM models with operational and sensor data for cost optimization
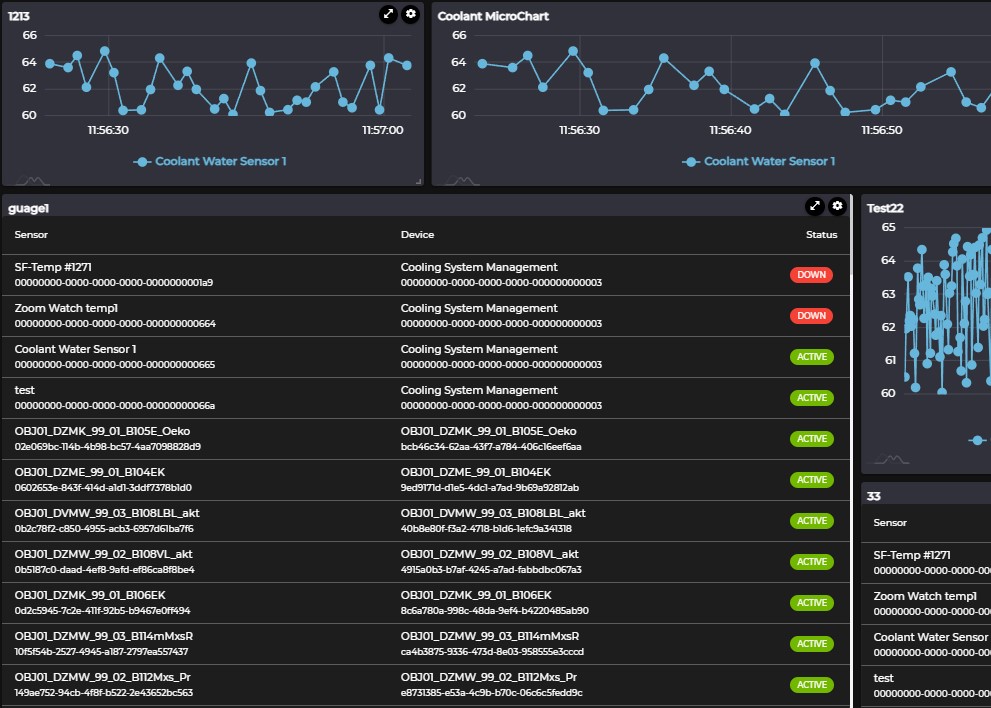
Based on data trends, ML models are created to predict patterns and trigger alerts when anomalies occur.
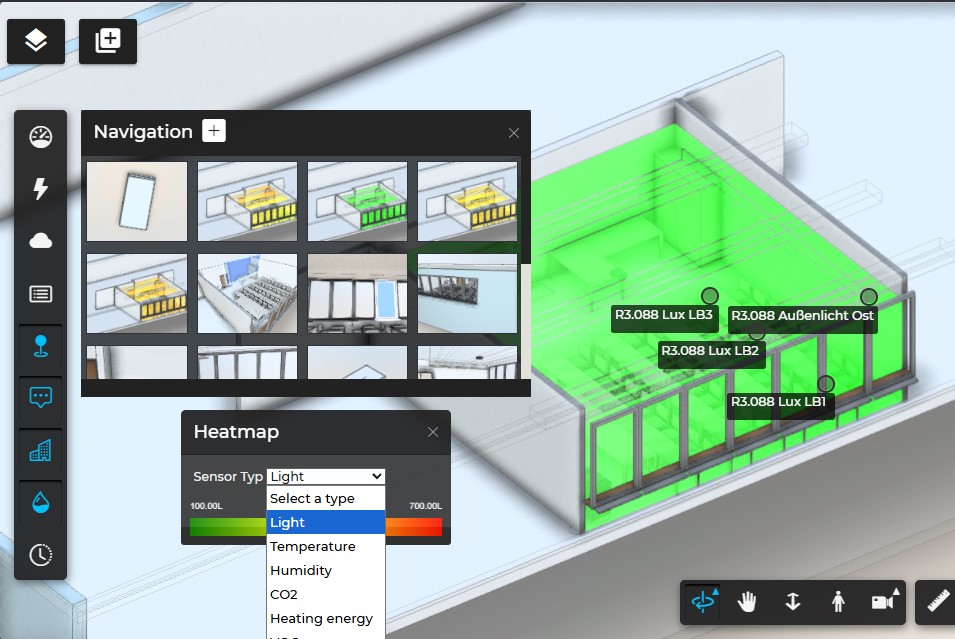
Why connect sensor data to the BIM model?
Real-time transparency
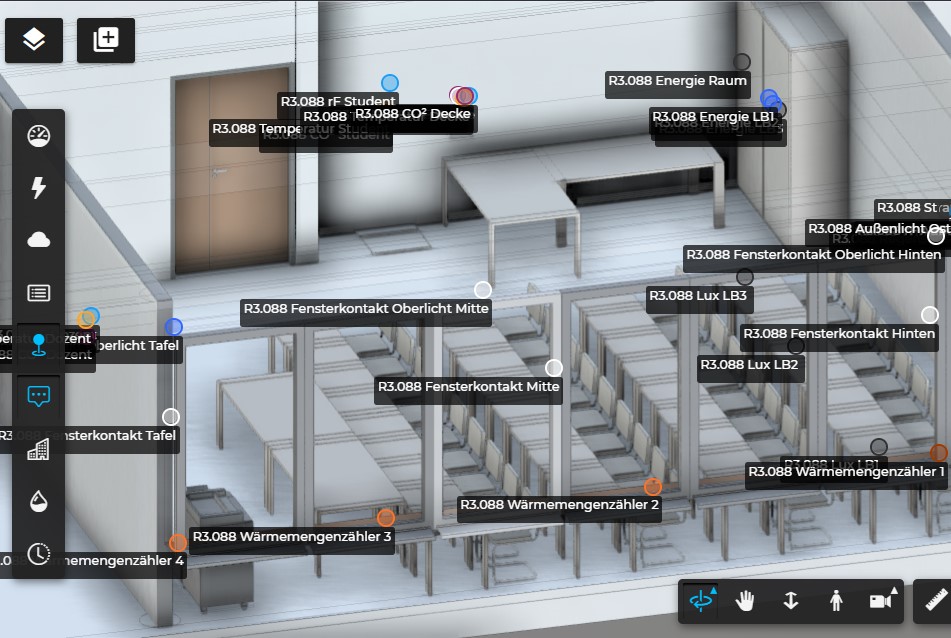
Temperature, air quality, energy usage, levels, and incidents are visualized directly in the model — by room, zone, or system.
Faster troubleshooting
Instead of a generic alert, the model shows exactly where the issue is, which zone and system are affected, and what to inspect.
Efficient energy management
Identify high-consumption areas, heating outside business hours, and optimization opportunities at a glance.
Optimized facility management
Teams see equipment locations, maintenance intervals, and historical issues inside the model, making operations more predictable.
Predictive maintenance
Long-term sensor data reveals patterns before pumps, fans, or elevators fail — enabling action before downtime.
Better decision-making
A live BIM model is understandable for all stakeholders and supports data-driven investment decisions.
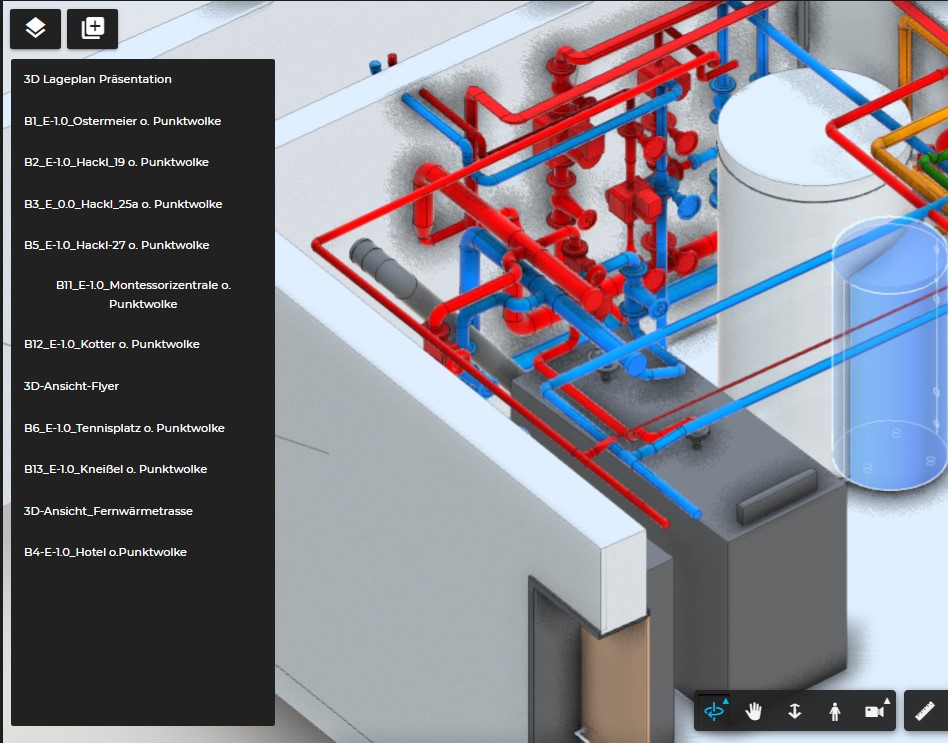
What is BIM?
BIM (Building Information Modeling) is a methodology that represents a building as a digital 3D model enriched with all relevant information.
- Geometry (rooms, walls, doors, technical systems, piping)
- Materials, costs, and lifecycle data
- Technical systems (heating, ventilation, elevators, etc.)
BIM is not a single tool. It is a shared digital information space where architects, planners, operators, and service providers collaborate.
Project snapshots